
When milliseconds matter and your users expect ChatGPT-level experiences.
The frameworks we have covered so far, LangChain, LlamaIndex, Haystack, are Python-first tools designed for backend AI pipelines. They excel at document processing, complex retrieval strategies, and server-side orchestration.
Vercel AI SDK takes a fundamentally different approach. It is TypeScript-first, built for the web, and optimized for one thing above all else: streaming.
When a user asks a question in a modern AI interface, they expect to see tokens appear in real-time, not a loading spinner followed by a wall of text. This streaming-first mentality permeates every design decision in the AI SDK. It is not an afterthought bolted onto a traditional request-response model; it is the foundation.
Let me be direct: Vercel AI SDK is not a complete RAG framework. It does not have document loaders, chunking utilities, or built-in vector store integrations like LangChain or LlamaIndex.
What it provides instead are primitives: low-level building blocks for building AI-native web applications. These primitives handle the hard parts of streaming AI responses, managing conversation state in React, and deploying to edge runtimes, while leaving the RAG architecture decisions to you.
This is a feature, not a limitation. By focusing on what web frameworks do best, AI SDK avoids the abstraction overhead that frustrates developers in more comprehensive frameworks. You get exactly what you need, nothing more.
Vercel AI SDK is the right choice when:
If you are coming from LangChain (Part 2) or LlamaIndex (Part 3):
| Aspect | LangChain/LlamaIndex | Vercel AI SDK |
|---|---|---|
| Language | Python-first | TypeScript-first |
| Focus | Complete RAG pipeline | UI primitives for AI |
| Streaming | Supported (add-on) | Core architecture |
| Document processing | Extensive built-in | Bring your own |
| Vector stores | 50+ integrations | Manual integration |
| React integration | Limited | First-class hooks |
| Edge runtime | Difficult | Native support |
The AI SDK is modular. Install the core package plus your preferred AI provider:
# Core SDK
npm install ai
# Provider packages (install what you need)
npm install @ai-sdk/openai # OpenAI
npm install @ai-sdk/anthropic # Anthropic Claude
npm install @ai-sdk/google # Google Gemini
npm install @ai-sdk/mistral # Mistral AI
npm install @ai-sdk/amazon-bedrock # AWS BedrockFor a typical Next.js RAG application:
npm install ai @ai-sdk/openaiCreate a .env.local file in your Next.js project root:
# Required: Your AI provider API key
OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-proj-...
# Optional: For other providers
ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=sk-ant-...
GOOGLE_GENERATIVE_AI_API_KEY=...
# For vector database (choose one)
PINECONE_API_KEY=...
UPSTASH_VECTOR_REST_URL=...
UPSTASH_VECTOR_REST_TOKEN=...
# For PostgreSQL with pgvector
DATABASE_URL=postgresql://user:password@host:5432/dbA well-organized AI SDK project:
app/
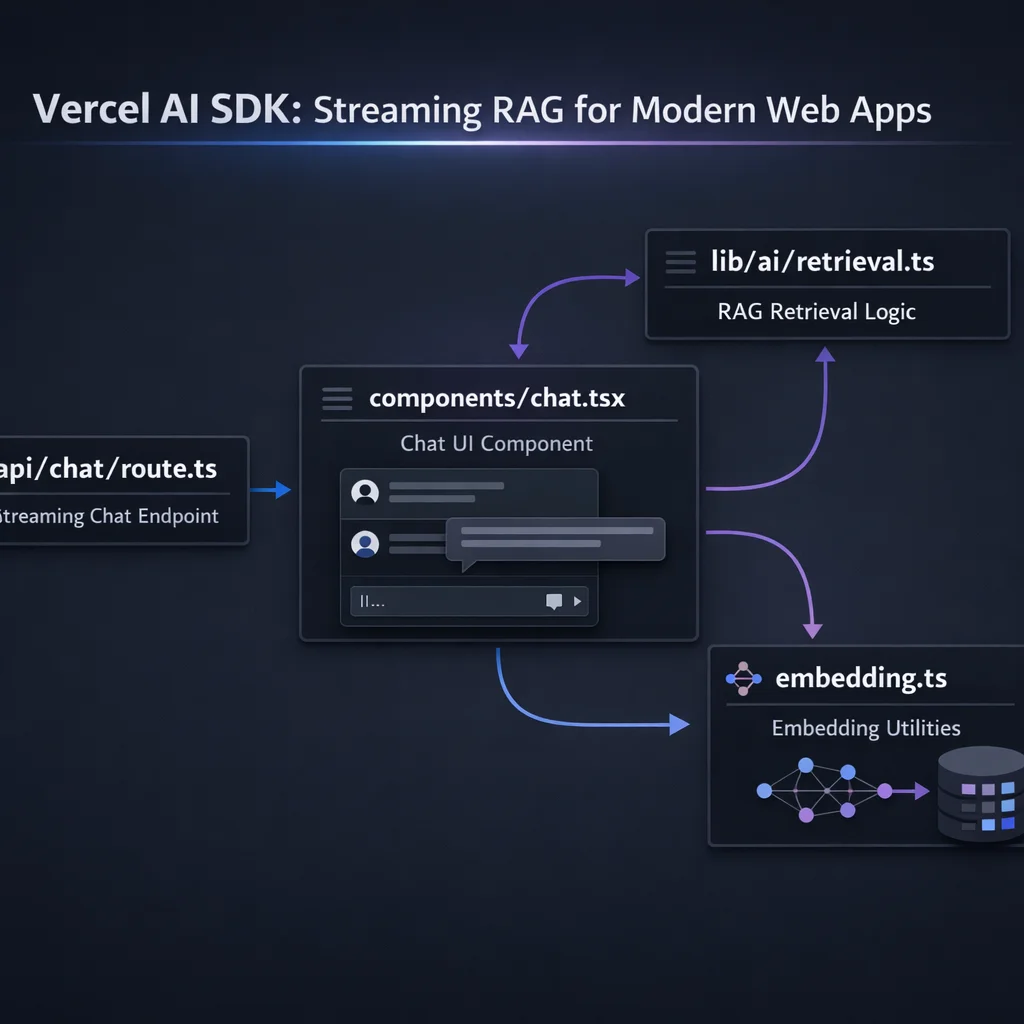AI SDK provides three categories of primitives: server-side functions for generation, client-side hooks for React, and utilities for managing AI interactions.
The streamText function is the core primitive for streaming text generation:
// app/api/chat/route.ts
import { streamText } from 'ai';
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
export async function POST(req: Request) {
const { messages } = await req.json();
const result = streamText({
model: openai('gpt-4o'),
messages,
system: 'You are a helpful assistant.',
});
return result.toDataStreamResponse();
}This creates a streaming endpoint that sends tokens as they are generated. The toDataStreamResponse() method handles all the complexity of Server-Sent Events, backpressure, and proper HTTP headers.
When you do not need streaming (batch processing, background tasks):
import { generateText } from 'ai';
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
const { text } = await generateText({
model: openai('gpt-4o'),
prompt: 'Summarize the key points of this document...',
});
console.log(text);The useChat hook manages the entire conversation lifecycle on the client:
// app/components/chat.tsx
'use client';
import { useChat } from 'ai/react';
export function Chat() {
const { messages, input, handleInputChange, handleSubmit, isLoading } = useChat();
return (
<div className="flex flex-col h-screen">
<div className="flex-1 overflow-y-auto p-4 space-y-4">
{messages.map((message) => (
<div
key={message.id}
className={`p-3 rounded-lg ${
message.role === 'user'
? 'bg-blue-100 ml-auto max-w-[80%]'
: 'bg-gray-100 mr-auto max-w-[80%]'
}`}
>
{message.content}
</div>
))}
{isLoading && (
<div className="text-gray-500">Thinking...</div>
)}
</div>
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit} className="p-4 border-t">
<input
value={input}
onChange={handleInputChange}
placeholder="Ask a question..."
className="w-full p-2 border rounded"
/>
</form>
</div>
);
}The hook automatically:
For single-turn completions (not conversations):
'use client';
import { useCompletion } from 'ai/react';
export function Summarizer() {
const { completion, input, handleInputChange, handleSubmit, isLoading } =
useCompletion({
api: '/api/summarize',
});
return (
<div>
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<textarea
value={input}
onChange={handleInputChange}
placeholder="Paste text to summarize..."
className="w-full h-48 p-2 border rounded"
/>
<button type="submit" disabled={isLoading}>
{isLoading ? 'Summarizing...' : 'Summarize'}
</button>
</form>
{completion && (
<div className="mt-4 p-4 bg-gray-50 rounded">
<h3 className="font-bold">Summary:</h3>
<p>{completion}</p>
</div>
)}
</div>
);
}AI SDK does not provide RAG components out of the box. Instead, you build RAG by combining AI SDK's streaming primitives with your choice of vector database and retrieval logic.
The simplest RAG pattern: retrieve documents before calling streamText:
// app/api/chat/route.ts
import { streamText } from 'ai';
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
import { retrieveDocuments } from '@/lib/ai/retrieval';
export async function POST(req: Request) {
const { messages } = await req.json();
const lastMessage = messages[messages.length - 1].content;
// 1. Retrieve relevant documents
const documents = await retrieveDocuments(lastMessage);
// 2. Format context
const context = documents
.map((doc, i) => `[${i + 1}] ${doc.content}`)
.join('\n\n');
// 3. Build system prompt with context
const systemPrompt = `You are a helpful assistant. Answer questions based on the following context.
If the context doesn't contain relevant information, say so.
Context:
${context}
Always cite your sources using [1], [2], etc.`;
// 4. Stream the response
const result = streamText({
model: openai('gpt-4o'),
system: systemPrompt,
messages,
});
return result.toDataStreamResponse();
}A more sophisticated approach uses AI SDK's tool calling feature. The model decides when to retrieve:
// app/api/chat/route.ts
import { streamText, tool } from 'ai';
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
import { z } from 'zod';
import { searchDocuments } from '@/lib/ai/retrieval';
export async function POST(req: Request) {
const { messages } = await req.json();
const result = streamText({
model: openai('gpt-4o'),
system: `You are a helpful assistant with access to a knowledge base.
Use the searchKnowledgeBase tool to find relevant information before answering questions.
Always cite your sources.`,
messages,
tools: {
searchKnowledgeBase: tool({
description: 'Search the knowledge base for relevant documents',
parameters: z.object({
query: z.string().describe('The search query'),
limit: z.number().default(5).describe('Number of results to return'),
}),
execute: async ({ query, limit }) => {
const results = await searchDocuments(query, limit);
return results.map((doc) => ({
title: doc.metadata.title,
content: doc.content,
source: doc.metadata.source,
}));
},
}),
},
maxSteps: 3, // Allow up to 3 tool calls per request
});
return result.toDataStreamResponse();
}The maxSteps parameter enables multi-step reasoning: the model can search, review results, search again with a refined query, and then answer.
For advanced control, use the wrapLanguageModel function to inject context automatically:
// lib/ai/rag-middleware.ts
import { wrapLanguageModel, type LanguageModelV1Middleware } from 'ai';
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
import { retrieveDocuments } from './retrieval';
const ragMiddleware: LanguageModelV1Middleware = {
transformParams: async ({ params }) => {
// Extract the last user message
const lastUserMessage = params.prompt
.filter((p) => p.role === 'user')
.pop();
if (!lastUserMessage || lastUserMessage.content[0].type !== 'text') {
return params;
}
const query = lastUserMessage.content[0].text;
// Retrieve relevant documents
const documents = await retrieveDocuments(query);
// Inject context into system prompt
const context = documents.map((d) => d.content).join('\n\n---\n\n');
const enhancedSystem = `${params.prompt.find((p) => p.role === 'system')?.content || ''}
Relevant context from the knowledge base:
${context}
Use this context to inform your response. Cite sources when applicable.`;
return {
...params,
prompt: params.prompt.map((p) =>
p.role === 'system' ? { ...p, content: enhancedSystem } : p
),
};
},
};
export const ragModel = wrapLanguageModel({
model: openai('gpt-4o'),
middleware: ragMiddleware,
});Then use the wrapped model in your route:
// app/api/chat/route.ts
import { streamText } from 'ai';
import { ragModel } from '@/lib/ai/rag-middleware';
export async function POST(req: Request) {
const { messages } = await req.json();
const result = streamText({
model: ragModel,
system: 'You are a helpful assistant.',
messages,
});
return result.toDataStreamResponse();
}AI SDK does not include vector store clients. Here are integration patterns for popular options.
// lib/db/pinecone.ts
import { Pinecone } from '@pinecone-database/pinecone';
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
import { embed } from 'ai';
const pinecone = new Pinecone();
const index = pinecone.index('rag-documents');
export async function searchDocuments(query: string, limit: number = 5) {
// Generate embedding for query
const { embedding } = await embed({
model: openai.embedding('text-embedding-3-small'),
value: query,
});
// Search Pinecone
const results = await index.query({
vector: embedding,
topK: limit,
includeMetadata: true,
});
return results.matches.map((match) => ({
content: match.metadata?.content as string,
metadata: {
title: match.metadata?.title as string,
source: match.metadata?.source as string,
},
score: match.score,
}));
}
export async function indexDocument(
id: string,
content: string,
metadata: Record<string, string>
) {
const { embedding } = await embed({
model: openai.embedding('text-embedding-3-small'),
value: content,
});
await index.upsert([
{
id,
values: embedding,
metadata: { content, ...metadata },
},
]);
}Upstash Vector is particularly well-suited for edge deployments:
// lib/db/upstash.ts
import { Index } from '@upstash/vector';
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
import { embed } from 'ai';
const index = new Index({
url: process.env.UPSTASH_VECTOR_REST_URL!,
token: process.env.UPSTASH_VECTOR_REST_TOKEN!,
});
export async function searchDocuments(query: string, limit: number = 5) {
const { embedding } = await embed({
model: openai.embedding('text-embedding-3-small'),
value: query,
});
const results = await index.query({
vector: embedding,
topK: limit,
includeMetadata: true,
});
return results.map((result) => ({
content: result.metadata?.content as string,
metadata: result.metadata as Record<string, string>,
score: result.score,
}));
}For PostgreSQL-based applications:
// lib/db/pgvector.ts
import { drizzle } from 'drizzle-orm/node-postgres';
import { pgTable, text, vector, uuid } from 'drizzle-orm/pg-core';
import { cosineDistance, desc, sql } from 'drizzle-orm';
import { embed } from 'ai';
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
import { Pool } from 'pg';
// Schema definition
export const documents = pgTable('documents', {
id: uuid('id').primaryKey().defaultRandom(),
content: text('content').notNull(),
title: text('title'),
source: text('source'),
embedding: vector('embedding', { dimensions: 1536 }),
});
const pool = new Pool({ connectionString: process.env.DATABASE_URL });
const db = drizzle(pool);
export async function searchDocuments(query: string, limit: number = 5) {
const { embedding } = await embed({
model: openai.embedding('text-embedding-3-small'),
value: query,
});
const results = await db
.select({
id: documents.id,
content: documents.content,
title: documents.title,
source: documents.source,
similarity: sql<number>`1 - (${cosineDistance(documents.embedding, embedding)})`,
})
.from(documents)
.orderBy(desc(sql`1 - (${cosineDistance(documents.embedding, embedding)})`))
.limit(limit);
return results;
}
export async function indexDocument(
content: string,
title: string,
source: string
) {
const { embedding } = await embed({
model: openai.embedding('text-embedding-3-small'),
value: content,
});
await db.insert(documents).values({
content,
title,
source,
embedding,
});
}AI SDK's streaming capabilities shine in the UI layer. Here are patterns for building responsive, real-time interfaces.
The default useChat behavior streams tokens automatically:
'use client';
import { useChat } from 'ai/react';
export function StreamingChat() {
const { messages, input, handleInputChange, handleSubmit, isLoading } = useChat();
return (
<div className="max-w-2xl mx-auto p-4">
<div className="space-y-4 mb-4">
{messages.map((message) => (
<div key={message.id} className="flex gap-3">
<div className="font-bold">
{message.role === 'user' ? 'You:' : 'AI:'}
</div>
<div className="flex-1">
{/* Content streams in automatically */}
{message.content}
{/* Show cursor while streaming */}
{isLoading && message.role === 'assistant' && (
<span className="animate-pulse">|</span>
)}
</div>
</div>
))}
</div>
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit} className="flex gap-2">
<input
value={input}
onChange={handleInputChange}
placeholder="Ask about our documentation..."
className="flex-1 p-2 border rounded"
/>
<button
type="submit"
disabled={isLoading}
className="px-4 py-2 bg-blue-500 text-white rounded disabled:opacity-50"
>
Send
</button>
</form>
</div>
);
}When using tool-based retrieval, display sources alongside the response:
'use client';
import { useChat, type Message } from 'ai/react';
interface Source {
title: string;
content: string;
source: string;
}
export function RAGChat() {
const { messages, input, handleInputChange, handleSubmit, isLoading } = useChat();
// Extract sources from tool calls
const getSourcesFromMessage = (message: Message): Source[] => {
if (!message.toolInvocations) return [];
return message.toolInvocations
.filter((tool) => tool.toolName === 'searchKnowledgeBase' && tool.state === 'result')
.flatMap((tool) => tool.result as Source[]);
};
return (
<div className="max-w-4xl mx-auto p-4">
<div className="space-y-6 mb-4">
{messages.map((message) => {
const sources = getSourcesFromMessage(message);
return (
<div key={message.id}>
<div className="flex gap-3">
<div className="font-bold w-16">
{message.role === 'user' ? 'You:' : 'AI:'}
</div>
<div className="flex-1">{message.content}</div>
</div>
{/* Display sources */}
{sources.length > 0 && (
<div className="ml-16 mt-2 p-3 bg-gray-50 rounded-lg">
<div className="text-sm font-medium text-gray-500 mb-2">
Sources:
</div>
<div className="space-y-2">
{sources.map((source, i) => (
<div key={i} className="text-sm">
<span className="font-medium">{source.title}</span>
<span className="text-gray-500 ml-2">
({source.source})
</span>
</div>
))}
</div>
</div>
)}
</div>
);
})}
</div>
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit} className="flex gap-2">
<input
value={input}
onChange={handleInputChange}
placeholder="Ask a question..."
className="flex-1 p-2 border rounded"
/>
<button type="submit" disabled={isLoading}>
{isLoading ? 'Searching...' : 'Ask'}
</button>
</form>
</div>
);
}Proper error handling for production applications:
'use client';
import { useChat } from 'ai/react';
import { useState } from 'react';
export function RobustChat() {
const [retryCount, setRetryCount] = useState(0);
const {
messages,
input,
handleInputChange,
handleSubmit,
isLoading,
error,
reload,
stop,
} = useChat({
onError: (error) => {
console.error('Chat error:', error);
// Log to your error tracking service
},
onFinish: () => {
setRetryCount(0);
},
});
const handleRetry = () => {
if (retryCount < 3) {
setRetryCount((prev) => prev + 1);
reload();
}
};
return (
<div className="max-w-2xl mx-auto p-4">
<div className="space-y-4 mb-4">
{messages.map((message) => (
<div key={message.id} className="p-3 rounded-lg bg-gray-100">
<div className="font-bold mb-1">
{message.role === 'user' ? 'You' : 'Assistant'}
</div>
<div>{message.content}</div>
</div>
))}
{/* Error state */}
{error && (
<div className="p-3 bg-red-100 border border-red-300 rounded-lg">
<div className="font-bold text-red-700">Error</div>
<div className="text-red-600 text-sm">{error.message}</div>
{retryCount < 3 && (
<button
onClick={handleRetry}
className="mt-2 text-sm text-red-700 underline"
>
Retry ({3 - retryCount} attempts remaining)
</button>
)}
</div>
)}
</div>
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit} className="flex gap-2">
<input
value={input}
onChange={handleInputChange}
placeholder="Ask a question..."
className="flex-1 p-2 border rounded"
disabled={isLoading}
/>
{isLoading ? (
<button
type="button"
onClick={stop}
className="px-4 py-2 bg-red-500 text-white rounded"
>
Stop
</button>
) : (
<button
type="submit"
className="px-4 py-2 bg-blue-500 text-white rounded"
>
Send
</button>
)}
</form>
</div>
);
}One of AI SDK's killer features is native edge runtime support. This enables sub-100ms cold starts and global distribution.
// app/api/chat/route.ts
import { streamText } from 'ai';
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
// Enable edge runtime
export const runtime = 'edge';
export async function POST(req: Request) {
const { messages } = await req.json();
const result = streamText({
model: openai('gpt-4o'),
messages,
});
return result.toDataStreamResponse();
}That single line (export const runtime = 'edge') deploys your AI endpoint to Vercel's global edge network.
Not all vector databases work on the edge. Here is what does:
| Vector Store | Edge Compatible | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Upstash Vector | Yes | REST API, perfect for edge |
| Pinecone | Yes | REST API |
| pgvector | No | Requires TCP connections |
| FAISS | No | Requires Node.js runtime |
For edge deployments, prefer HTTP-based vector stores:
// app/api/chat/route.ts
import { streamText } from 'ai';
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
import { Index } from '@upstash/vector';
export const runtime = 'edge';
const vectorIndex = new Index({
url: process.env.UPSTASH_VECTOR_REST_URL!,
token: process.env.UPSTASH_VECTOR_REST_TOKEN!,
});
export async function POST(req: Request) {
const { messages } = await req.json();
const query = messages[messages.length - 1].content;
// Edge-compatible retrieval
const embedding = await generateEmbedding(query);
const results = await vectorIndex.query({
vector: embedding,
topK: 5,
includeMetadata: true,
});
const context = results.map((r) => r.metadata?.content).join('\n\n');
const result = streamText({
model: openai('gpt-4o'),
system: `Answer based on this context:\n\n${context}`,
messages,
});
return result.toDataStreamResponse();
}For applications that need both edge speed and server capabilities:
// app/api/chat/route.ts (edge - user-facing)
export const runtime = 'edge';
// Fast streaming responses for end users
// app/api/index/route.ts (node - background processing)
export const runtime = 'nodejs';
// Document indexing with full Node.js capabilitiesFor production deployments, you need more than just streaming. AI SDK integrates with gateway solutions for rate limiting, failover, and observability.
// lib/ai/rate-limit.ts
import { Ratelimit } from '@upstash/ratelimit';
import { Redis } from '@upstash/redis';
const ratelimit = new Ratelimit({
redis: Redis.fromEnv(),
limiter: Ratelimit.slidingWindow(10, '1 m'), // 10 requests per minute
analytics: true,
});
export async function checkRateLimit(identifier: string) {
const { success, limit, remaining, reset } = await ratelimit.limit(identifier);
return {
success,
headers: {
'X-RateLimit-Limit': limit.toString(),
'X-RateLimit-Remaining': remaining.toString(),
'X-RateLimit-Reset': reset.toString(),
},
};
}// app/api/chat/route.ts
import { streamText } from 'ai';
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
import { checkRateLimit } from '@/lib/ai/rate-limit';
export const runtime = 'edge';
export async function POST(req: Request) {
// Get user identifier (IP, user ID, API key)
const ip = req.headers.get('x-forwarded-for') || 'anonymous';
const { success, headers } = await checkRateLimit(ip);
if (!success) {
return new Response('Rate limit exceeded', {
status: 429,
headers,
});
}
const { messages } = await req.json();
const result = streamText({
model: openai('gpt-4o'),
messages,
});
const response = result.toDataStreamResponse();
// Add rate limit headers
Object.entries(headers).forEach(([key, value]) => {
response.headers.set(key, value);
});
return response;
}Automatically fall back to alternative providers. Note that streamText returns immediately without throwing errors synchronously - errors become part of the stream. This requires a different pattern than traditional try-catch:
// lib/ai/failover.ts
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
import { anthropic } from '@ai-sdk/anthropic';
import { generateText, type CoreMessage } from 'ai';
const providers = [
{ name: 'openai', model: openai('gpt-4o') },
{ name: 'anthropic', model: anthropic('claude-sonnet-4-20250514') },
];
// For non-streaming with proper failover
export async function generateWithFailover(
messages: CoreMessage[],
system?: string
) {
let lastError: Error | null = null;
for (const { name, model } of providers) {
try {
console.log(`Attempting ${name}...`);
// generateText throws on error, unlike streamText
const result = await generateText({
model,
messages,
system,
});
return result;
} catch (error) {
console.error(`${name} failed:`, error);
lastError = error as Error;
}
}
throw lastError || new Error('All providers failed');
}
// For streaming, use the middleware pattern instead
// See: https://sdk.vercel.ai/docs/ai-sdk-core/middlewareImportant: For streaming failover, consider using the AI SDK middleware pattern or implementing circuit breaker logic at the infrastructure level. The
streamTextfunction doesn't throw synchronously, so wrapping it in try-catch won't catch provider errors.
AI SDK integrates with Vercel's observability features:
// app/api/chat/route.ts
import { streamText } from 'ai';
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
export async function POST(req: Request) {
const { messages } = await req.json();
const result = streamText({
model: openai('gpt-4o'),
messages,
// Enable experimental telemetry
experimental_telemetry: {
isEnabled: true,
functionId: 'rag-chat',
metadata: {
userId: req.headers.get('x-user-id') || 'anonymous',
},
},
});
return result.toDataStreamResponse();
}This sends telemetry data to Vercel's dashboard for monitoring latency, token usage, and errors.
AI costs can spiral without proper controls. Here are patterns for managing costs with AI SDK.
Track and limit token usage:
// lib/ai/tokens.ts
import { encoding_for_model } from 'tiktoken';
const encoder = encoding_for_model('gpt-4o');
export function countTokens(text: string): number {
return encoder.encode(text).length;
}
export function estimateCost(
inputTokens: number,
outputTokens: number,
model: string = 'gpt-4o'
): number {
const pricing: Record<string, { input: number; output: number }> = {
'gpt-4o': { input: 0.0025, output: 0.01 }, // per 1K tokens
'gpt-4o-mini': { input: 0.00015, output: 0.0006 },
'claude-sonnet-4-20250514': { input: 0.003, output: 0.015 },
};
const rates = pricing[model] || pricing['gpt-4o'];
return (inputTokens * rates.input + outputTokens * rates.output) / 1000;
}Prevent context overflow and control costs:
// lib/ai/context.ts
import { type CoreMessage } from 'ai';
import { countTokens } from './tokens';
const MAX_CONTEXT_TOKENS = 8000; // Leave room for response
export function trimMessages(
messages: CoreMessage[],
systemPrompt: string
): CoreMessage[] {
const systemTokens = countTokens(systemPrompt);
let availableTokens = MAX_CONTEXT_TOKENS - systemTokens;
// Always keep the last message
const lastMessage = messages[messages.length - 1];
const lastMessageTokens = countTokens(
typeof lastMessage.content === 'string'
? lastMessage.content
: JSON.stringify(lastMessage.content)
);
availableTokens -= lastMessageTokens;
// Add messages from newest to oldest until we run out of tokens
const trimmedMessages: CoreMessage[] = [lastMessage];
for (let i = messages.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
const message = messages[i];
const content = typeof message.content === 'string'
? message.content
: JSON.stringify(message.content);
const tokens = countTokens(content);
if (tokens <= availableTokens) {
trimmedMessages.unshift(message);
availableTokens -= tokens;
} else {
break;
}
}
return trimmedMessages;
}Log usage for billing and analytics:
// app/api/chat/route.ts
import { streamText } from 'ai';
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
export async function POST(req: Request) {
const { messages, userId } = await req.json();
const result = streamText({
model: openai('gpt-4o'),
messages,
onFinish: async ({ usage }) => {
// Log to your database
await logUsage({
userId,
model: 'gpt-4o',
promptTokens: usage.promptTokens,
completionTokens: usage.completionTokens,
totalTokens: usage.totalTokens,
timestamp: new Date(),
});
},
});
return result.toDataStreamResponse();
}
async function logUsage(data: {
userId: string;
model: string;
promptTokens: number;
completionTokens: number;
totalTokens: number;
timestamp: Date;
}) {
// Implementation depends on your database
console.log('Usage:', data);
}Here is a production-ready RAG application using Next.js App Router and Vercel AI SDK:
app/
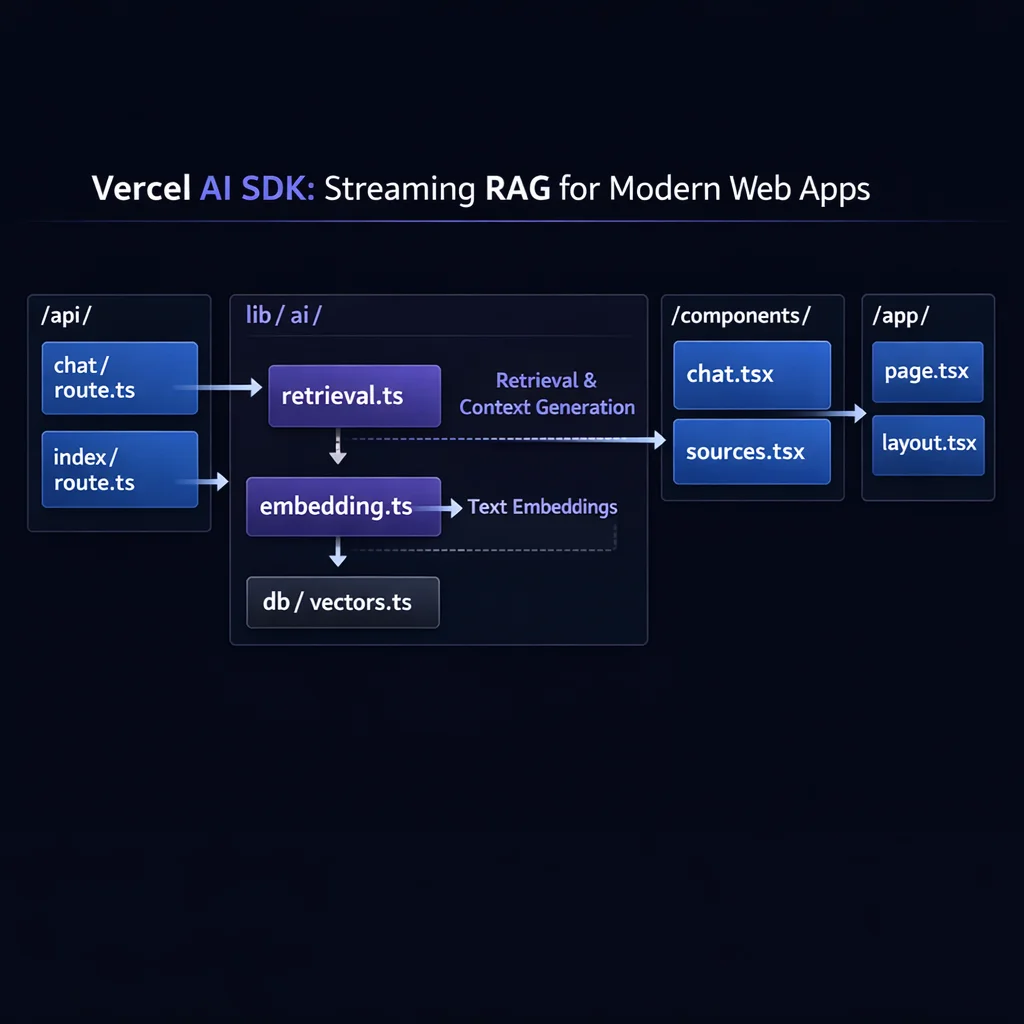// lib/db/vectors.ts
import { Index } from '@upstash/vector';
import { embed, embedMany } from 'ai';
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
const index = new Index({
url: process.env.UPSTASH_VECTOR_REST_URL!,
token: process.env.UPSTASH_VECTOR_REST_TOKEN!,
});
export interface Document {
id: string;
content: string;
metadata: {
title: string;
source: string;
[key: string]: string;
};
}
export async function searchDocuments(
query: string,
limit: number = 5
): Promise<Document[]> {
const { embedding } = await embed({
model: openai.embedding('text-embedding-3-small'),
value: query,
});
const results = await index.query({
vector: embedding,
topK: limit,
includeMetadata: true,
});
return results.map((result) => ({
id: result.id,
content: result.metadata?.content as string,
metadata: {
title: result.metadata?.title as string,
source: result.metadata?.source as string,
},
}));
}
export async function indexDocuments(documents: Document[]): Promise<void> {
const { embeddings } = await embedMany({
model: openai.embedding('text-embedding-3-small'),
values: documents.map((d) => d.content),
});
await index.upsert(
documents.map((doc, i) => ({
id: doc.id,
vector: embeddings[i],
metadata: {
content: doc.content,
...doc.metadata,
},
}))
);
}// app/api/chat/route.ts
import { streamText, tool } from 'ai';
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
import { z } from 'zod';
import { searchDocuments } from '@/lib/db/vectors';
export const runtime = 'edge';
export async function POST(req: Request) {
const { messages } = await req.json();
const result = streamText({
model: openai('gpt-4o'),
system: `You are a helpful assistant with access to a knowledge base.
When users ask questions:
1. Use the searchKnowledgeBase tool to find relevant information
2. Synthesize the information into a clear, accurate answer
3. Always cite your sources using the source names provided
4. If no relevant information is found, say so honestly
Be concise but thorough. Prefer accuracy over comprehensiveness.`,
messages,
tools: {
searchKnowledgeBase: tool({
description:
'Search the knowledge base for relevant documents. Use this for any factual questions.',
parameters: z.object({
query: z
.string()
.describe('The search query - be specific and descriptive'),
limit: z
.number()
.min(1)
.max(10)
.default(5)
.describe('Number of results to return'),
}),
execute: async ({ query, limit }) => {
const results = await searchDocuments(query, limit);
return results.map((doc) => ({
title: doc.metadata.title,
content: doc.content,
source: doc.metadata.source,
}));
},
}),
},
maxSteps: 3,
});
return result.toDataStreamResponse();
}// app/api/index/route.ts
import { NextResponse } from 'next/server';
import { indexDocuments, type Document } from '@/lib/db/vectors';
// Use Node.js runtime for indexing (more capabilities)
export const runtime = 'nodejs';
export async function POST(req: Request) {
try {
const { documents } = (await req.json()) as { documents: Document[] };
if (!documents || !Array.isArray(documents)) {
return NextResponse.json(
{ error: 'Invalid documents array' },
{ status: 400 }
);
}
await indexDocuments(documents);
return NextResponse.json({
success: true,
indexed: documents.length,
});
} catch (error) {
console.error('Indexing error:', error);
return NextResponse.json(
{ error: 'Failed to index documents' },
{ status: 500 }
);
}
}// app/components/chat.tsx
'use client';
import { useChat, type Message } from 'ai/react';
import { useState } from 'react';
interface Source {
title: string;
content: string;
source: string;
}
export function Chat() {
const {
messages,
input,
handleInputChange,
handleSubmit,
isLoading,
error,
reload,
stop,
} = useChat({
api: '/api/chat',
});
const getSourcesFromMessage = (message: Message): Source[] => {
if (!message.toolInvocations) return [];
return message.toolInvocations
.filter(
(tool) =>
tool.toolName === 'searchKnowledgeBase' && tool.state === 'result'
)
.flatMap((tool) => tool.result as Source[]);
};
return (
<div className="flex flex-col h-screen max-w-4xl mx-auto">
{/* Messages */}
<div className="flex-1 overflow-y-auto p-4 space-y-6">
{messages.length === 0 && (
<div className="text-center text-gray-500 mt-8">
<h2 className="text-xl font-semibold mb-2">
Welcome to the Knowledge Base
</h2>
<p>Ask any question about our documentation.</p>
</div>
)}
{messages.map((message) => {
const sources = getSourcesFromMessage(message);
return (
<div key={message.id} className="space-y-2">
<div
className={`flex gap-3 ${
message.role === 'user' ? 'justify-end' : 'justify-start'
}`}
>
<div
className={`max-w-[80%] p-4 rounded-lg ${
message.role === 'user'
? 'bg-blue-500 text-white'
: 'bg-gray-100'
}`}
>
<div className="whitespace-pre-wrap">{message.content}</div>
</div>
</div>
{/* Sources */}
{sources.length > 0 && (
<div className="ml-4 p-3 bg-gray-50 rounded-lg border">
<div className="text-sm font-medium text-gray-600 mb-2">
Sources used:
</div>
<div className="space-y-1">
{sources.slice(0, 3).map((source, i) => (
<div key={i} className="text-sm text-gray-700">
<span className="font-medium">{source.title}</span>
<span className="text-gray-500 ml-2">
- {source.source}
</span>
</div>
))}
{sources.length > 3 && (
<div className="text-sm text-gray-500">
+{sources.length - 3} more sources
</div>
)}
</div>
</div>
)}
</div>
);
})}
{/* Loading state */}
{isLoading && (
<div className="flex gap-3">
<div className="bg-gray-100 p-4 rounded-lg">
<div className="flex items-center gap-2">
<div className="w-2 h-2 bg-gray-400 rounded-full animate-bounce" />
<div
className="w-2 h-2 bg-gray-400 rounded-full animate-bounce"
style={{ animationDelay: '0.2s' }}
/>
<div
className="w-2 h-2 bg-gray-400 rounded-full animate-bounce"
style={{ animationDelay: '0.4s' }}
/>
</div>
</div>
</div>
)}
{/* Error state */}
{error && (
<div className="bg-red-50 border border-red-200 p-4 rounded-lg">
<div className="text-red-700 font-medium">Error</div>
<div className="text-red-600 text-sm">{error.message}</div>
<button
onClick={() => reload()}
className="mt-2 text-sm text-red-700 underline"
>
Try again
</button>
</div>
)}
</div>
{/* Input form */}
<div className="border-t p-4">
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit} className="flex gap-2">
<input
value={input}
onChange={handleInputChange}
placeholder="Ask a question about our documentation..."
className="flex-1 p-3 border rounded-lg focus:outline-none focus:ring-2 focus:ring-blue-500"
disabled={isLoading}
/>
{isLoading ? (
<button
type="button"
onClick={stop}
className="px-6 py-3 bg-red-500 text-white rounded-lg hover:bg-red-600"
>
Stop
</button>
) : (
<button
type="submit"
className="px-6 py-3 bg-blue-500 text-white rounded-lg hover:bg-blue-600 disabled:opacity-50"
disabled={!input.trim()}
>
Send
</button>
)}
</form>
</div>
</div>
);
}// app/page.tsx
import { Chat } from './components/chat';
export default function Home() {
return (
<main className="min-h-screen bg-white">
<Chat />
</main>
);
}// app/layout.tsx
import type { Metadata } from 'next';
import './globals.css';
export const metadata: Metadata = {
title: 'Knowledge Base Chat',
description: 'AI-powered documentation assistant',
};
export default function RootLayout({
children,
}: {
children: React.ReactNode;
}) {
return (
<html lang="en">
<body>{children}</body>
</html>
);
}Vercel AI SDK offers a fundamentally different approach to RAG than Python-centric frameworks:
Strengths:
Trade-offs:
When to Choose AI SDK:
This article covered building streaming RAG applications with Vercel AI SDK. Continue with the series:
For production deployments, also explore:
This is Part 7 of the "Building RAG Systems: A Platform-by-Platform Guide" series. Previous: AWS Bedrock Knowledge Bases. Next: Advanced Retrieval: Hybrid Search and Reranking.
Discover more content: